There are mainly five types of joints are used in welding for joining two parts of metal.
Now let we discuss joints in details :
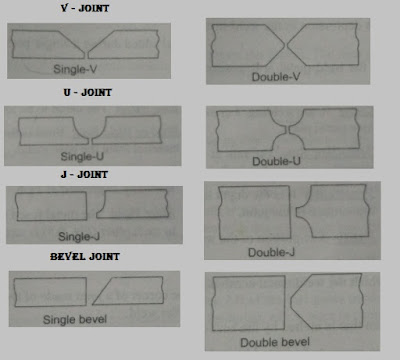
In single joint welding is to be carried out only one side while in double joints the edge preparations are used when welding is to be carried out both sides.
- Butt Joint
- Corner Joint
- Lap Joint
- Tee Joint
- Edge Joint
Now let we discuss joints in details :
- Butt joint :
A butt joint is a technique in which two metal parts lie in the same plane and are jointed at their edges without any special shaping.
- Corner joint :
A cornet joint is a technique in which two metal parts located at right angles to one another in the form of the shape of L are joined at the centre of the angle.
It is used to connect two parts together and forming a corner.
- Lap joint :
A lap joint is a technique in which two metal parts are overlapped that are joined.
- Tee joint :
A tea joint is a technique in which two metal parts those surfaces are located approximately 900 to each other that can be welded from both sides.
- Edge joint :
An edge joint is a technique in which two metal parts joined by two edges and making a corner.
All these types of joints used when the thickness of the two metal parts to be joined is small so that heat of welding penetrates the full depth of the joint.
However, when the thickness increases, it becomes necessary to prepare the edge in such a way that the heat is able to penetrate the entire depth.
For very thick metal plates, the welding needs to be done from both sides. To provide necessary access into the joint, it could be made as to the following joints :
In single joint welding is to be carried out only one side while in double joints the edge preparations are used when welding is to be carried out both sides.